Evolution is the study of how characteristics of a species change over time. Changes can happen slowly over many generations in response to environmental changes or quickly through selective breeding. This guide covers the important information students need to know, provides links to products and free digital resources, and includes suggestions for labs that reinforce student learning. We have gathered a variety of products and resources to help you teach this concept. They include:
Classification and Taxonomy
Organisms were first classified by Aristotle based on their observable structures and characteristics. He is given credit for dividing organisms into two groups, plants and animals. Taxonomic relationships are visualized with cladograms setting the groundwork for evolutionary relationships. Today classification is more complex, and relationships between organisms are also based on shared DNA. These kits model the process of classification and cladogram construction.
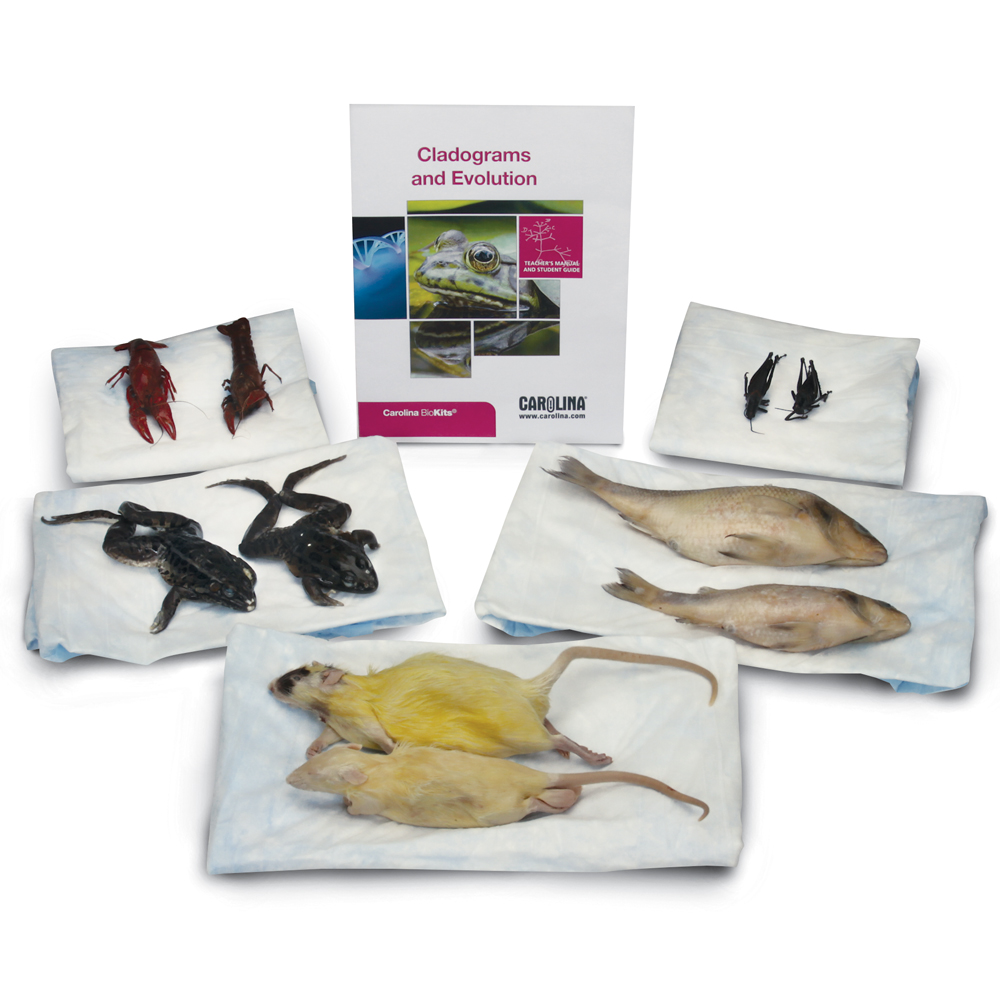
Cladograms and Evolution Kit #221042
Beginning
Easy to Perform Requires little to no prior knowledge
Students propose evolutionary relationships using 2 lines of evidence. First, students examine the external anatomical characteristics of 5 different preserved specimens. Based on morphological similarities, they create a cladogram. Students are then provided data about differences in the sequence of amino acids in a protein that the animals share. The students construct an additional cladogram based on this molecular information. Considering both morphological characteristics and genetic information, students propose evolutionary relationships among the animals and try to explain any discrepancies between their 2 cladograms. The question that drives students’ investigations is, “How can we evaluate and communicate evidence of evolutionary relationships among a group of organisms?”
Classification of Organisms Kit #132580
Beginning
Easy to Perform Requires little to no prior knowledge
A class of 30 students working in groups of 4 observe and record data on the characteristics of several organisms belonging to different animal phyla. The data is then used to rank the organisms from simple to complex and create a simple phylogenetic tree. In the process, students reinforce concepts presented in their textbooks and apply their knowledge and understanding through discussion with classmates.
Inquiries in Science: Classifying Across the Kingdoms Kit #251015
Beginning
Easy to Perform Requires little to no prior knowledge
In this laboratory activity, students use a guided-inquiry technique as they work together to explore classification of organisms. They study binomial nomenclature and work with dichotomous keys to determine the kingdom and further classification of various organisms. Kit includes enough materials (live organisms, 15 self-study cards to enhance viewing the organisms with a microscope [not included], slides, coverslips, inoculating loops, hand lenses, pipets, and more) for at least 30 students working in groups.
Structure and Function Kit: The Evolution of Eukaryotes, Prokaryotes, and Viruses #131210
Beginning
Easy to Perform Requires little to no prior knowledge
In the first activity, students design a cell or virus by selecting traceable structures and organelles, and then name the type of drawn cell or virus and describe its characteristics. Next, students trade drawings and practice classification using a dichotomous key. In the second activity, students practice microscope techniques and hone their observation skills by documenting various morphologies of bacteria and the parasitism of tobacco mosaic virus on a leaf. In the third activity, students observe Amoeba feeding on Chilomonas, allowing them to visualize functioning organelles and the concept of endocytosis. Provided background information illuminates the leading theories of evolution and the relationship among eukaryotes, prokaryotes, and viruses.
Natural Selection
Organisms adapt and change in response to changing environmental conditions. Organisms that are better able to survive, live longer and produce more offspring, increase the frequency of the adaptive trait within the population. These kits help students model and explain that process.
Natural Selection Kit #171200
Beginning
Easy to Perform Requires little to no prior knowledge
The dramatic increase in the frequency of dark moths, and corresponding decrease in the frequency of light moths, in 19th-century England’s peppered moth population define the investigative phenomenon. Students model 5 generations of moths, gathering evidence of genotype and allele frequencies as environmental variables change. They compare calculated Hardy-Weinberg frequencies for a population in genetic equilibrium with the observed frequencies of their model. After their statistical analysis, students revise their claim about the cause of the phenomenon.
Natural Selection with Drosophila Kit #171995
Beginning
Easy to Perform Requires little to no prior knowledge
Bringing a realistic model of natural selection and evolution into your classroom has never been easier. Using the model organism Drosophila melanogaster, students introduce a single advantageous “mutation” (red eyes) into a population of white-eyed “ancestral” strain flies. They then observe and calculate the new trait’s spread and the shift in population phenotypes over generations.
Carolina Investigations® for Use with AP® Biology: Population Genetics and Evolution #747510
Beginning
Easy to Perform Requires little to no prior knowledge
Students examine the genetics of a population and consider how allelic frequencies can provide evidence about the evolution of species. Students model a population using cards to represent individual alleles, then collect phenotypic data from a population of Wisconsin Fast Plants®. Using direct counting and the Hardy-Weinberg equation, students determine the frequencies of the 2 alleles. Then students design and conduct an experiment to investigate population genetics further.
Inquiries in Science®: Simulating the Darwinian Theory #251013
Beginning
Easy to Perform Requires little to no prior knowledge
Allow students to explore the theory of evolution and witness the process through simulations. Students use a guided-inquiry technique as they work in groups to simulate natural selection through predation. Experiments address natural selection, variety within species, overpopulation, genetic variability, and gene pools.
Artificial Selection
Artificial selection, sometimes called selective breeding, is the intentional selection of breeding stock to increase the proportion of desirable traits in a population. Artificial selection is common in animals and plants and tends to be faster than natural selection. The kits below are inquiries into selective breeding in Wisconsin Fast Plants and brine shrimp.
Wisconsin Fast Plants® Investigating Artificial Selection Using Plant Populations Kit #158776
Intermediate
Easy to Perform Requires some background knowledge
This open-ended experiment utilizes inquiry and cooperative learning to study the process of science, natural selection, plant breeding, genetics, plant growth, and reproduction. Starting with the standard Wisconsin Fast Plants® seed stock, students use a quick, simple method to count leaf hairs and select the hairiest plants to produce seed for the next generation. Comparison of the average number and distribution of leaf hairs in both generations enables students to describe the pattern of inheritance for hairiness and to test a hypothesis.
Carolina Investigations® for Use with AP® Biology: Natural Selection #747520
Intermediate
Easy to Perform Requires some background knowledge
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.
Kits That Cover All Topics Above
Evolution Models and Manipulatives
Other Evolution Products
We offer a number of products that will help facilitate your evolution lessons.
Additional Evolution Support
Use these free resources to supplement your instruction about evolution.
- Introduce your students to Cladogram Construction.
- Observe extraterrestrial Natural Selection.
- Analyze data from Galapagos Ground Finch.
- Investigate Natural Selection with Wisconsin Fast Plants.
- Study Natural Selection in 50 minutes.
- Investigate about the Diversity of the Eye.
- Make a Scientific Claim.
- Learn about Turkeys and Their Domestication.
Evolution Videos
Looking for videos to enhance your osmosis and diffusion instruction? Try one of these.
Buying Guides
Choosing the appropriate equipment for your labs can be a challenging task. Our buying guides are designed to make your decisions easy.
For More Guidance
These are our top picks. If you don’t see what you’re looking for, we’ll be happy to help you find the right activities and kits to simplify your planning and implementation. If you have questions, please contact us at product@carolina.com.