Hydrogen Spectrum Activity
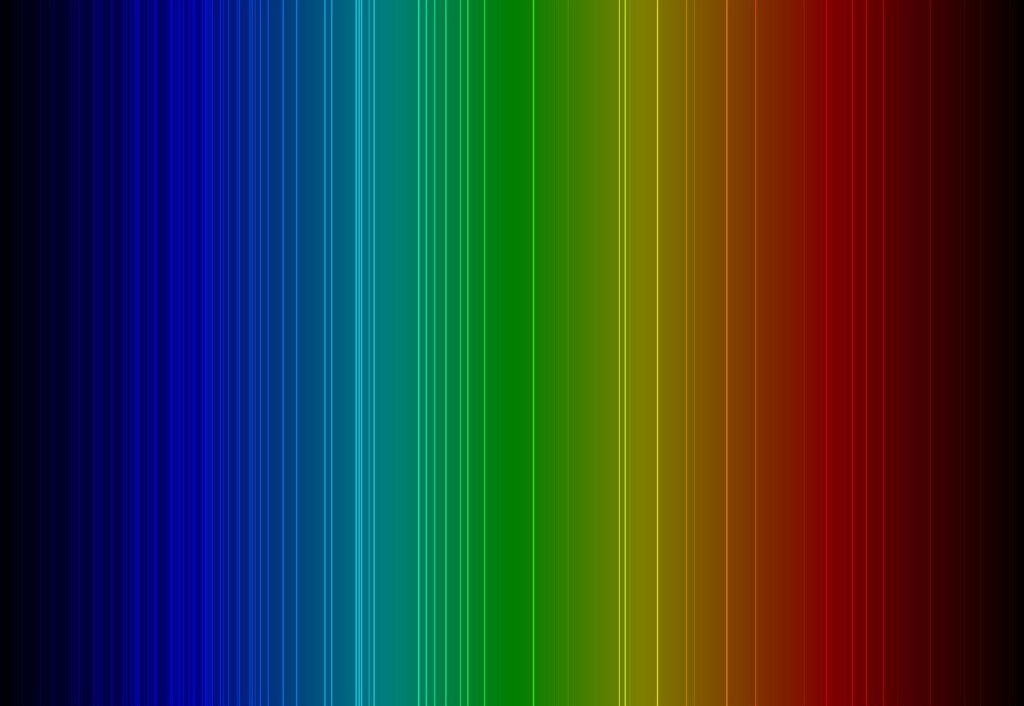

Objective To observe hydrogen’s emission spectrum and to verify that the Bohr model of the hydrogen atom accounts for the line positions in hydrogen’s emission spectrum. Introduction Bohr’s model of the atom explains hydrogen’s spectrum but does not satisfactorily explain atoms that have more than 1 electron and proton and is, therefore, not the currently […]
Most Popular Physics Kits That Electrify Students’ Lab Experiences

Your momentum might change if you knew that you could cover your physics course, start to finish, with Carolina’s top-selling physics kits. These 10 kits offer students hands-on experiments, model generation, and data analysis, while meeting your physics course standards. Repeatedly chosen by thousands of teachers, these kits can help you electrify your students’ lab experiences.
Investigating Phenomena: How Can You Balance an Object?

Carolina Phenomenon Phenomena-driven science! Phenomena are observable, naturally occurring events that are everywhere and spark student questions and investigations. Ask students to observe the DCI-linked phenomenon in the video and complete the attached student sheet prior to remote learning discussions. Observations: Carefully watch the balancing bird video. Gather all the evidence you can from the video, and […]
Egg Vacuum Activity
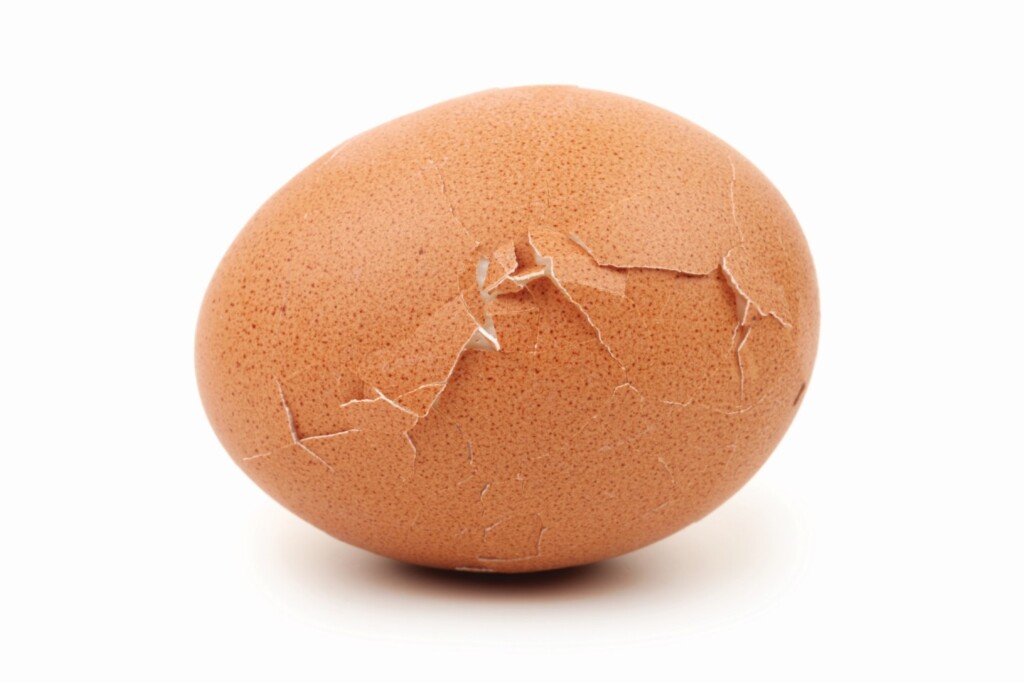

If you are looking for an attention-getting demonstration of the gas laws for physical science students at any grade level, this is it. Basic equipment includes a hard-boiled egg, an Erlenmeyer flask, and burning piece of paper. Materials needed Erlenmeyer Flask, 1 L, narrow mouth Egg, hard-boiled, shell removed Paper Lighter Tongs Safety Goggles Gloves […]
Make the Invisible Visible

Detecting IR Light with a Smart Phone The sun actually sends out more light than the part we see. Just past visible violet light is ultraviolet (UV) light, and just past visible red light is infrared (IR) light. Neither is visible to the human eye. Infrared light does not depend on visible light–IR light can […]
Optics of the Human Eye
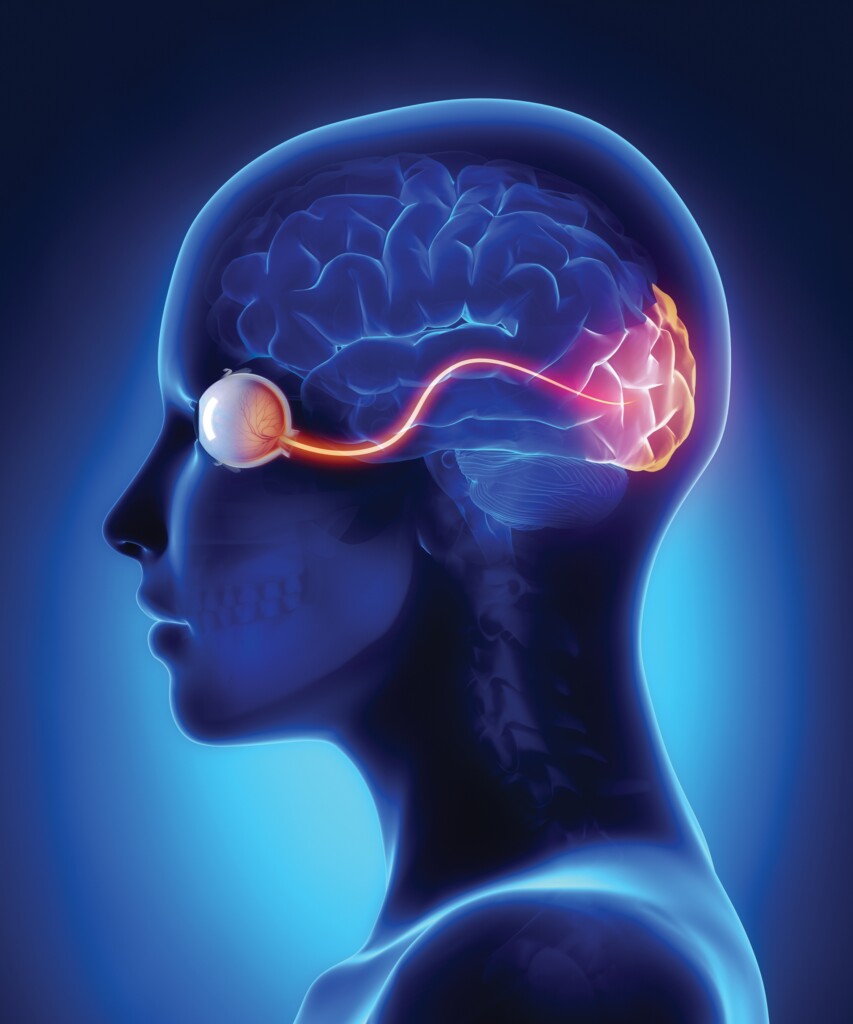
Background Geometric optics explains how optical devices (such as lenses and mirrors) create images by considering that light travels in rays, which are straight lines emanating from a light source or reflected from an object. A ray diagram is a useful tool in geometric optics; it describes images formed by lenses or mirrors. A ray […]
The Conical Pendulum

An Experiment in Circular Motion and Centripetal Acceleration The conical pendulum lab allows students to investigate the physics and mathematics of uniform circular motion. A motorized, plastic plane* is suspended from a thin string and “flies” in a circular path with a constant speed. The plane and the supporting string trace a conical pendulum. Students […]
A Brief Overview of Gravity and Gravitational Force

An introduction to Newton’s Law of Gravitation, specetime geometry, and quantum gravity. Gravity The word gravity has many definitions. As defined by dictionary.com, gravity means “the force of attraction by which terrestrial bodies tend to fall toward the center of the earth,” or “heaviness or weight,” or “serious or critical nature,” among other definitions (Dictionary.com, […]
Derivation of the Kinematics Equation
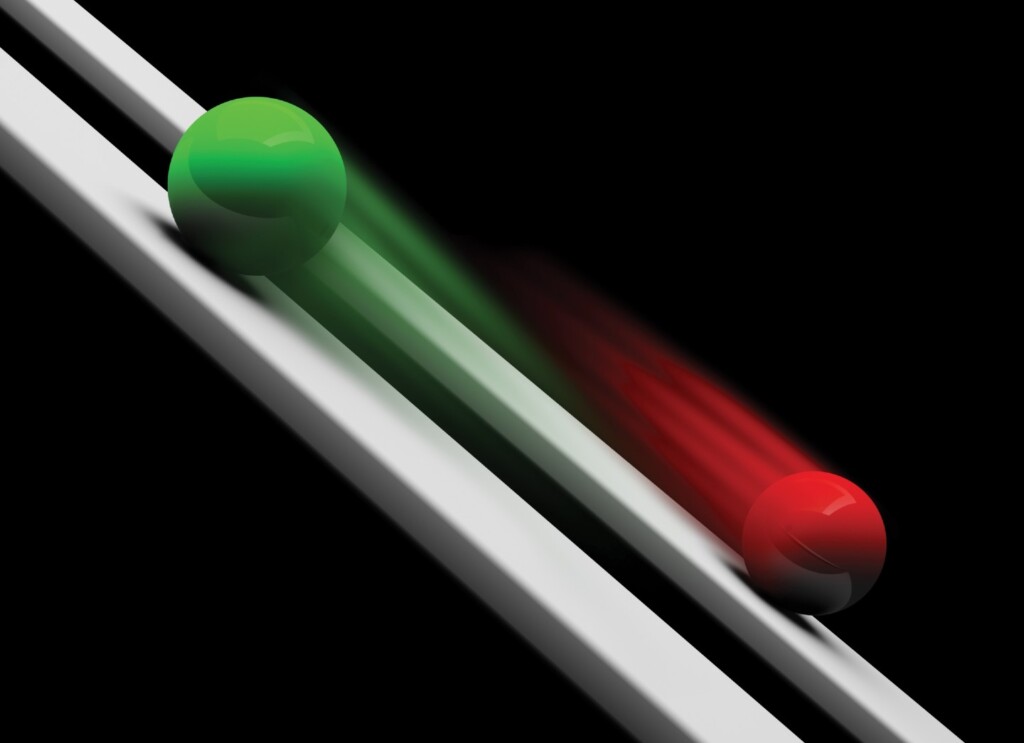

High school physics courses usually begin with a study of classical mechanics. Early in the course students are introduced to the equations of motion, the kinematics equations. Kinematics Kinematics is the study of the motion of objects without concern for the forces causing the motion. These familiar equations allow students to analyze and predict the […]
