Introduction to Blood Types
CAROLINA LABSHEETS Quick Links Close Quick Links Open Quick Links Overview NGSS Objective Materials Procedures & Prep Kit Overview NGSS Objective Materials Procedures & Prep Kit Overview In this lab, students are introduced to the human ABO blood groups. The activity is designed for use with our Carolina® Synthetic Blood, but it may also be performed […]
The Pressure’s On: Creating and Using Models of Body Systems

Workshop Resources Life Science 6-12 Middle / High School Learn exciting and engaging ways to teach structure and function within body systems. Use hands-on labs to help students understand kidney function and interactions between the excretory system and cardiovascular system. Set up experiments, collect data, analyze results, and create models to build toward understanding the […]
Just Passing Through

In-Booth Demonstration Life Science 9-12 High School / College Cell membranes are semipermeable, meaning that only certain substances, based on the molecule’s size and electric charge, can pass through. Molecules passively move from areas of high concentration to areas of low concentration. Starch, which is a large molecule that cannot pass through most membranes, can […]
Diffusion—Molecules on the Move
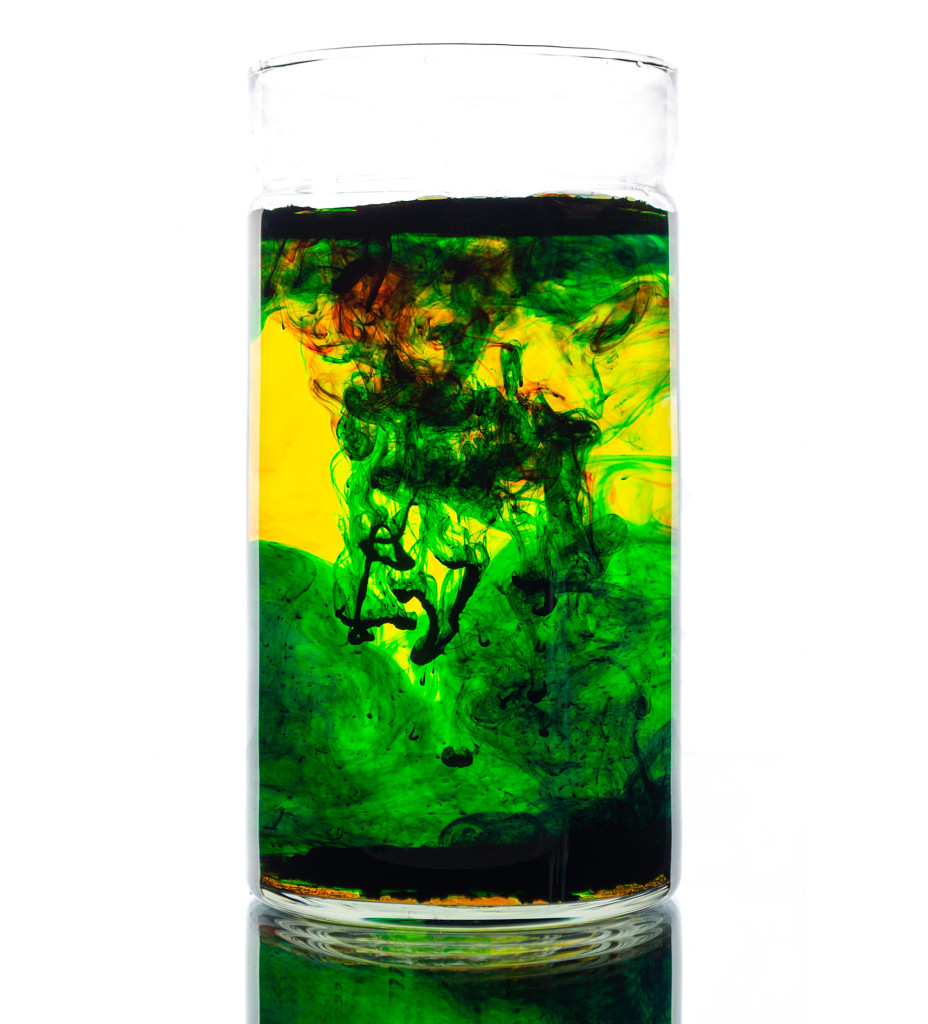

Diffusion: Molecules on the Move Dialysis tubing is an excellent way to simulate the cell membrane’s selective permeability. In this experiment, sealed dialysis tubing containing a test solution of albumin, glucose, sodium chloride, and starch is placed in a cup of distilled water. After 30 to 45 minutes, the tubing is removed from the cup […]
Osmosis Eggsperiment

Introduction 2-3 students per group Prep: 15 minutes Class: 15-45 minutes over 3 days Subject: Physiology Grade: 6-12 Water passes into and out of cells by a special type of diffusion called osmosis. Osmosis is the diffusion of water molecules across a selectively permeable membrane from an area of higher water concentration to an area of […]
Top-Selling Models by Body System
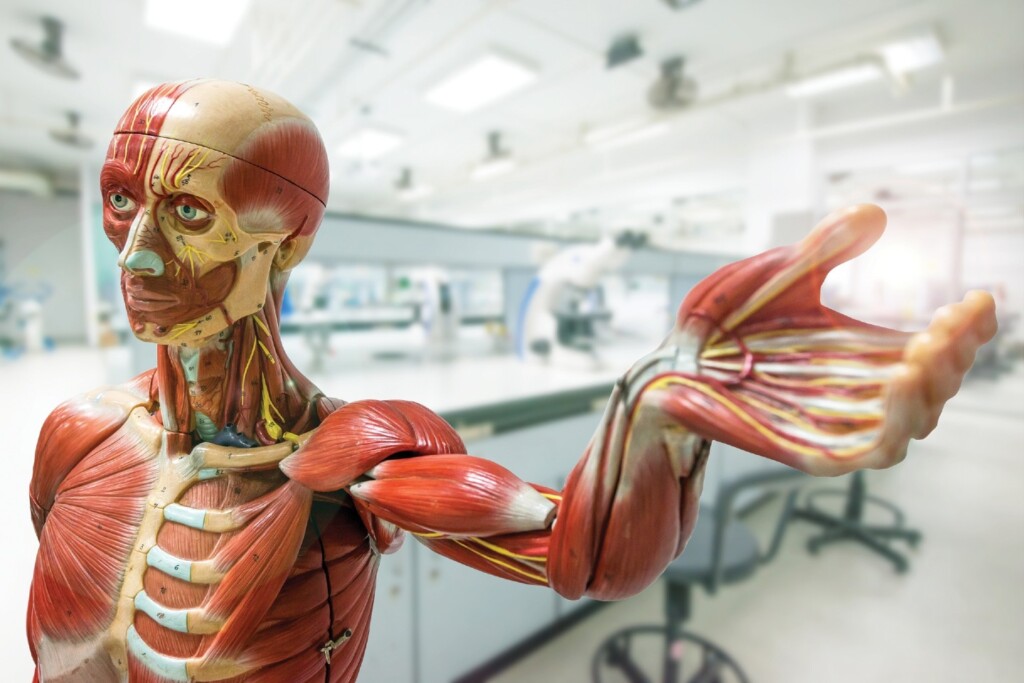

Anatomy and physiology courses benefit greatly from the use anatomical models and skeletons. Quality models show detailed morphology of organs and complete body systems. Models simplify the identification of anatomical structures, organ positioning within the body cavity, and the relationship between structure and function. Many models can be disassembled, allowing students to explore internal structures. Additionally, they are an excellent reference tool for identifying small and indistinct structures.
Body Systems

human body systems Bring science to life in your classroom with FREE, ready-to-use resources for teaching human body systems.Simply hover over the system you want to explore, and click to dive in! Each body system includes: • A visually engaging introductory infographic • A hands-on activity or informative article • A printable graphic organizer to […]
Developing and Analyzing Urine Samples as a Model of Kidney Function
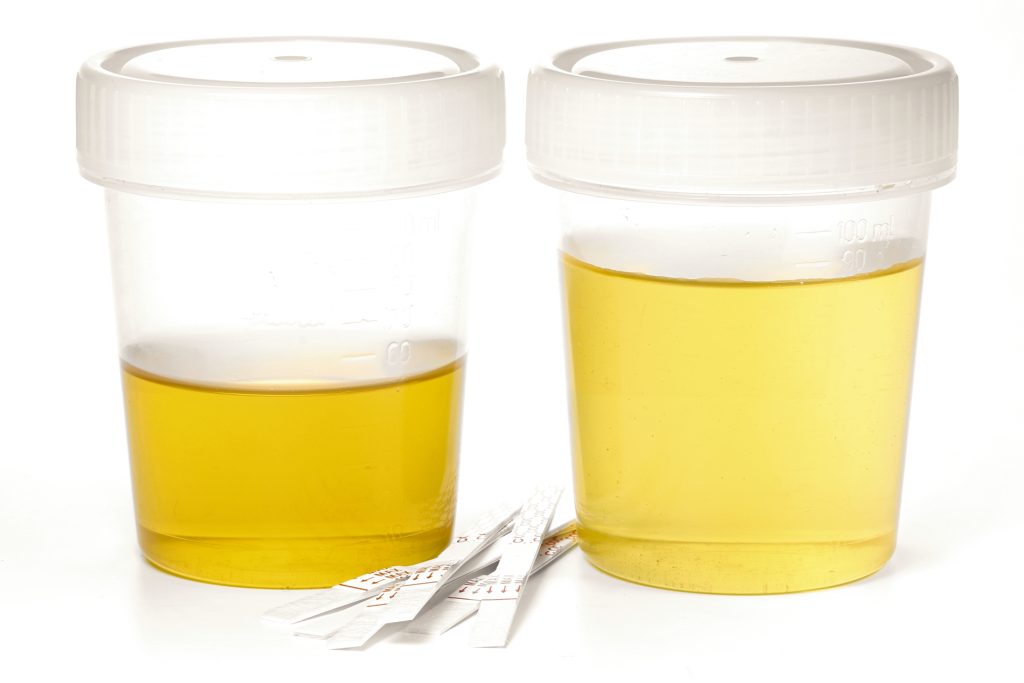

Abnormal urine composition often indicates disease or infection. Diabetes is often diagnosed after a patient has a positive test for glucose in the urine. Diabetes is the result of an inability to absorb glucose from the blood. The body compensates for these elevated blood glucose levels by filtering the glucose out through the kidneys; the excess glucose exits the body through the urine.
Using Histology Slides to Enhance Mammalian Dissection

There are 4 main types of tissue: epithelial, muscle, nervous, and connective. Each type has a particular function and can be found to some degree in most organs. In order to understand the structure and function of each type of tissue, it is important to view them microscopically. Many tissues viewed with the naked eye […]
Diffusion and Osmosis

All cells are bound by some type of permeable or semipermeable membrane that governs the ions, small molecules, and large molecules that enter and leave the cell. Diffusion is the general process of movement down a gradient that results in equal concentrations of solutes on both sides of the membrane. When water is the molecule entering or leaving the cell the process is osmosis. This guide breaks down the important information students need to know, provides links to products and free digital resources, and includes suggestions for hands-on-labs that reinforce student learning.
