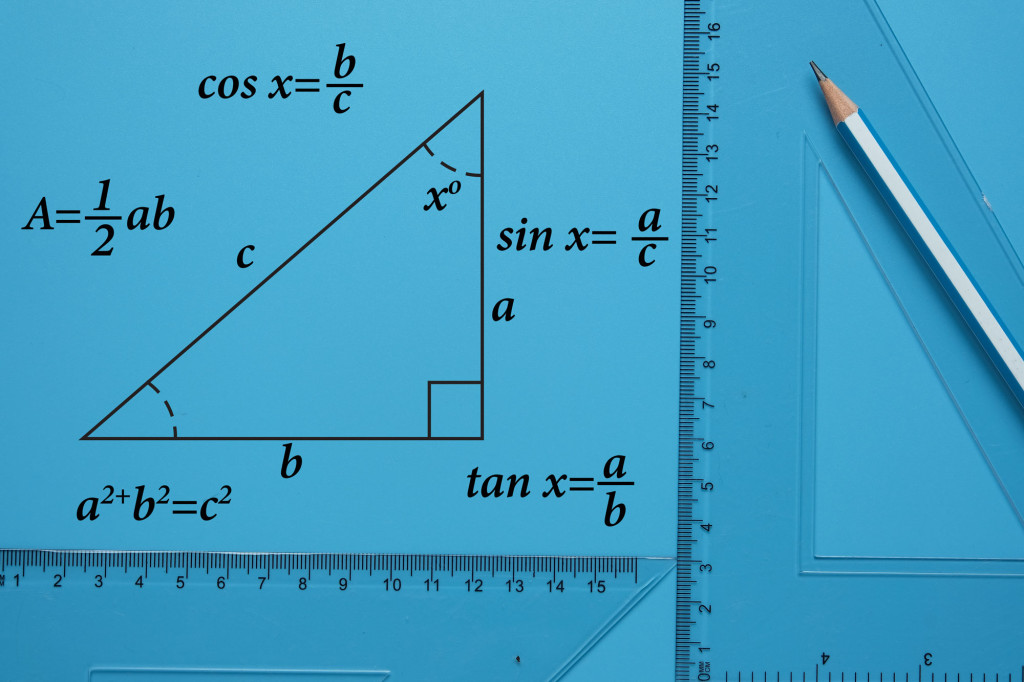This is a brief review of the basic trig functions Sine, Cosine, and Tangent as applied to a right triangle. A right triangle is a triangle where one angle measures 90°.
In order to calculate the Sine, Cosine and Tangent of an angle, first identify one angle. We will indicate this angle with the Greek letter “theta” or: Θ.
Label the sides of the triangle:
- The side opposite the right angle is the hypotenuse.
- The side opposite the angle Θ, is called the “opposite” side.
- The remaining side is called the “adjacent” side.

The sine of the angle, SIN Θ, is the ratio of the opposite side of the triangle to the hypotenuse of the triangle.

The cosine of the angle, COS Θ, is the ratio of the adjacent side of the triangle divided by the hypotenuse of the triangle.

The tangent of the angle, TAN Θ, is the ratio of the opposite side of the triangle divided by the adjacent side of the triangle.
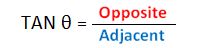
This mnemonic may help you remember:

These ratios are the same for any similar triangles, or any triangles with the same angle measurements.
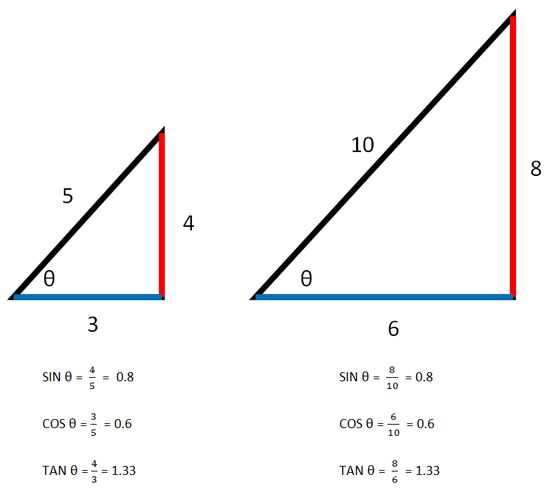
Note: The sine, cosine, and tangent of an angle have no units. If the measurements of the triangles above were in meters, then the units would cancel out.
Related Resources

Physical Science Math Review: Techniques, Formulae, and Constants

One in a Million: Using Serial Dilutions to Understand Concentration

Basic Right Triangle Trigonometry

How to Use Mathematics and Logical Routines

Using Science to Teach Math

Significant Figures
About The Author
Carolina Staff
Carolina is teamed with teachers and continually provides valuable resources–articles, activities, and how-to videos–to help teachers in their classroom.