Explore the structures and functions of muscle tissue
Essential Question
What are the structures and functions of muscle tissue?
Activity Objectives
-
- Observe muscle tissue.
- Explain movement based on muscle attachment.
- Practice dissection techniques.
Background
Cardiac muscle tissue is found in the heart. This type of muscle tissue contains a large amount of mitochondria, which are required for the lifelong contraction and relaxation of the heart muscle.
Skeletal muscle tissue is found throughout the body, attached to many bones and skin. This type of tissue is controlled voluntarily or involuntarily and allows us to move, maintain posture, and breathe.
Part A: Observe the structure of 3 types of muscle tissue.

Materials Needed ( Part A )
Use the images below to help you identify the prepared muscle slides given to you. Draw and label the tissue you observe under the microscope in the space provided.

Part B: Examine musculature of a chicken wing. Make comparisons to human musculature.
Materials Needed ( Part B )
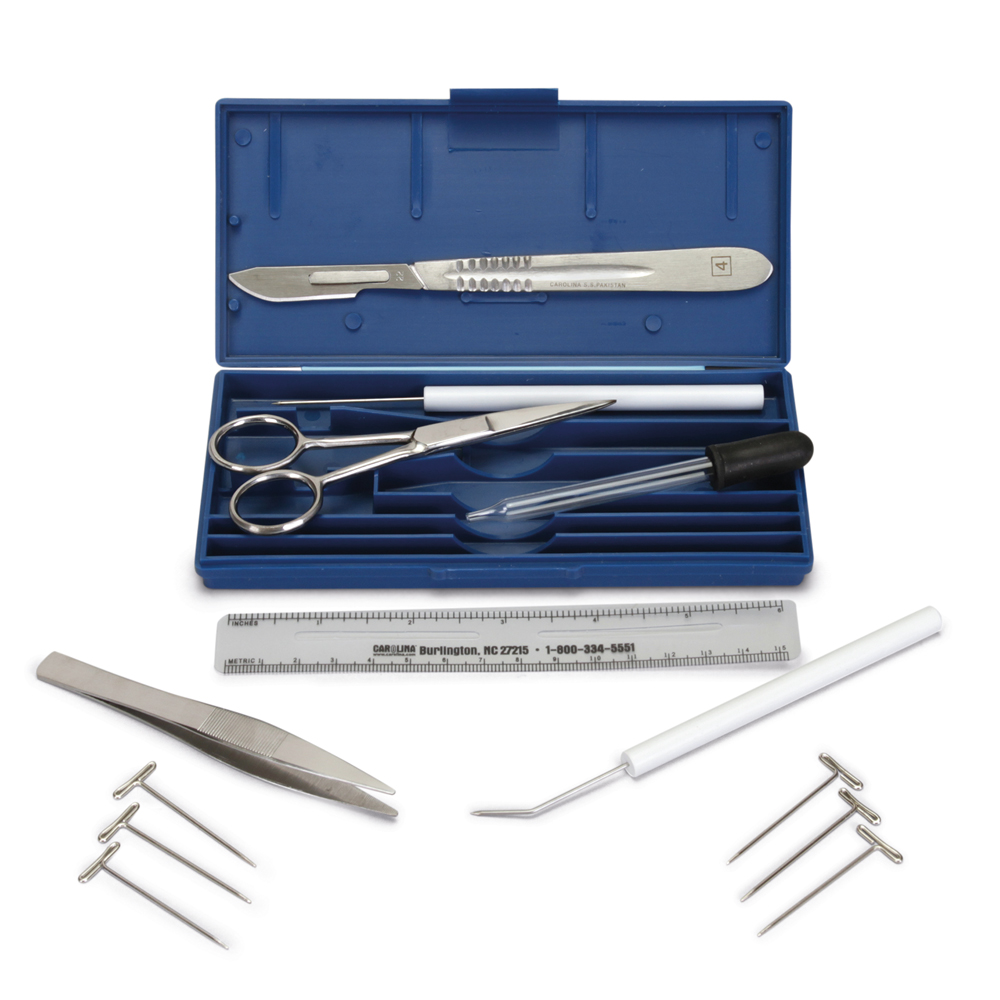
- Dissection kit (scissors, blunt tip probe, scalpel, dissecting pins, forceps)
- Dissection tray or mat
- Gloves
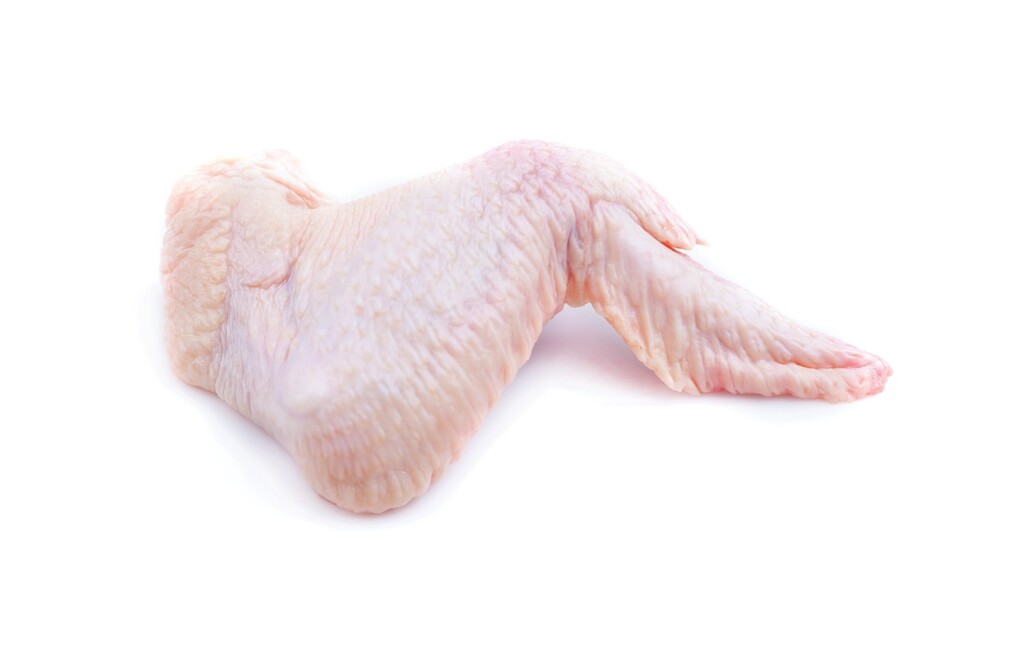
- Raw chicken wing
Dissection Supplies
Procedure
-
- Obtain dissection materials and the raw chicken wing.
- Observe the external anatomy of the wing.
- Feel the bone structure through the tissue.
- Using scissors, carefully lift the skin and make a small cut at the elbow.
- Carefully cut the skin from the elbow toward the wing tip and then toward the head of the humerus.
- Using forceps, gently pull the skin away from the muscle and cut the connective tissue between the skin and muscle. Be careful not to cut the muscle.
- Remove all skin.
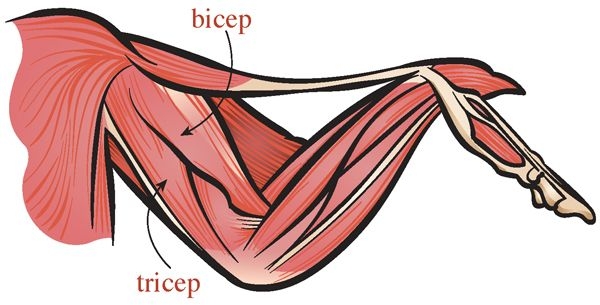
- Identify the bicep and tricep muscles in the wing.
- Gently separate the muscles from one another, leaving them attached to the bone.
- Carefully pull each of these muscles and observe the movement of the lower limb.
Discussion Questions
-
- Explain differences in the 3 types of muscle tissue you observed.
- Discuss how the structure of each muscle type is specific to muscle function.
- Describe the movement of the chicken wing produced by the bicep muscle.
- Describe the movement of the chicken wing produced by the tricep muscle.
- Working together, how does the wing musculature allow the chicken to fly?
Related Products
About The Author
Carolina Staff
Carolina is teamed with teachers and continually provides valuable resources–articles, activities, and how-to videos–to help teachers in their classroom.